Aging doesn’t guarantee that you will develop cataracts in one or both eyes. But as an often age-related condition, your risk certainly increases with age. Fortunately, it’s a highly treatable condition and can often be managed without surgery as a first step.
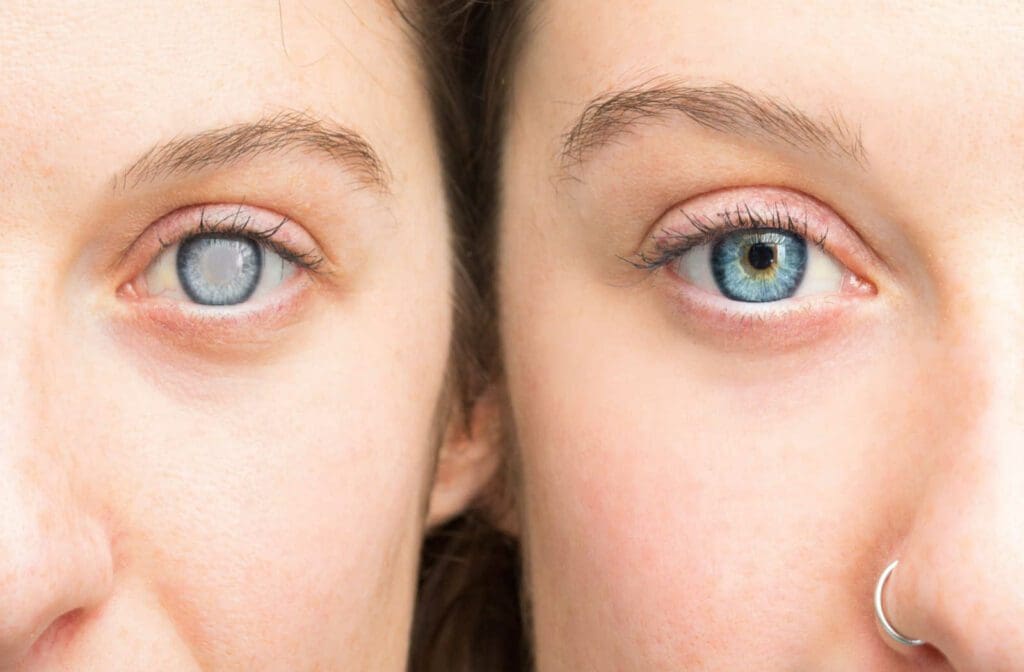
Regular eye examinations are an important part of early detection, especially if you’ve ever asked yourself whether you can have cataracts in one eye or both. And if you’re wondering whether you can have a cataract in one eye, the answer is yes. However, once you have a cataract, the chances are high that it won’t stop in one eye.
Table of Contents
What are Cataracts?
Our eyes have clear lenses that transmit light into the retina with minimal scattering. For many people, this lens grows cloudy or even changes color and becomes opaque over time; this is a cataract.
Several types of cataracts can begin in different areas of the lens. For example, some begin at the edge of your lens. These often go undiagnosed in their early development and can actually temporarily improve your reading vision. Or, you can have them develop in the center of the lens or behind it. Both of these types will change your vision quicker and more drastically.
The other possibility is a congenital cataract, which is a cataract that affects young children. Sometimes a child is born with a cataract because of a genetic predisposition. Other times they develop them very early in life, possibly due to infection or eye trauma.
Can You Have a Cataract in One Eye?
It’s 100% possible that you may develop a cataract in one eye. In addition, they are not an infectious disease, so they won’t spread to the other like an infection. However, in most cases of a person developing a cataract in one eye, they will almost always get one in the other eye too.
The other possibility is that you develop cataracts in both eyes simultaneously, But it’s possible they won’t grow at the same rate. This is another reason that cataracts often go undetected without an eye examination. When the cataract is worse in one eye, the other eye can sometimes overcompensate for vision loss so that you don’t notice it.
Why Do I Have a Cataract In Only One Eye?
Cataracts can sometimes develop in just one eye due to specific causes such as an eye injury, previous eye surgery, or certain medical conditions that affect only one eye. In some cases, genetics or random chance may play a role. While most cataracts are age-related and eventually affect both eyes, it’s not unusual for one eye to develop a cataract earlier than the other. Regular eye exams are important to monitor both eyes, even if only one is currently affected.

Blurry Vision in One Eye?
Cataracts often develop in one eye before the other. Let’s schedule an exam to determine if a cataract is causing your blurry vision and discuss treatment options.
- Comprehensive cataract screening for one-eye vision issues
- Lens options and treatment timelines explained
- Clear next steps for monitoring or treatment
Risk Factors for Cataracts
Age is a significant risk factor for cataracts. In fact, more than 50% of Americans over the age of 80 have cataracts or have had them removed with surgery. But age isn’t the only thing that increases our risk of developing cataracts.
Here are several things that can contribute to developing cataracts:
- Smoking (also a contributing factor to other eye conditions like glaucoma or diabetic retinopathy)
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Exposure to the sun without adequate UV protection
- Steroidal medications
- Family history of cataracts
- Obesity
- Underlying health issues like diabetes or heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Eye trauma or a previous surgery
Preventing Cataracts
Obviously, we can’t prevent aging, which is a major cause of cataracts, but some things you can do to reduce your risk of cataracts are:
- Regular eye examinations are the best proactive prevention
- Quitting smoking
- Proper management of other health issues like diabetes
- A healthy, balanced diet with lots of fruits and vegetables
- Wearing sunglasses with adequate UVA/UVB protection
- Reducing alcohol consumption
Treating Cataracts
In many cases, especially in the early development of cataracts, the condition can be managed without surgery. For example, a change in prescription for your glasses or contact lenses can sometimes compensate for vision loss.
Additionally, increasing light for activities like reading can also help. However, when the point comes that the cataracts are affecting your ability to perform your daily activities, it’s probably time to consult your ophthalmologist about your surgical options.
During cataract surgery, the eye doctor removes the old, cloudy lens and replaces it with an intraocular lens (IOL).
IOL Options
The IOL is one of the primary factors determining the result of cataract surgery. A common and typically cheapest option is a regular IOL that is custom-shaped to fit your unique cornea. However, there are some options in the market where an IOL is made to correct one or more focal points.
Not everyone is a candidate, though. So, your best bet is to discuss your options with your eye doctor. Once they’ve taken eye measurements during a cataract surgery consultation, they can present your available options to you and explain the pros and cons of each.
Frequently Asked Questions
If I have a cataract in one eye, will I definitely get one in the other eye?
Not necessarily, but the risk is higher. Cataracts are often age-related and tend to develop in both eyes over time, although not always at the same rate. Regular eye exams are important to monitor both eyes.
Are the symptoms of cataracts different if only one eye is affected?
Symptoms are generally the same—cloudy or blurred vision, glare, or color changes—but may be less noticeable if you have a cataract in one eye only. The unaffected eye can sometimes compensate, making the cataract harder to detect.
How are cataracts in one eye diagnosed?
Cataracts are diagnosed through a comprehensive eye exam. Your eye doctor will use special tests to check your lens for cloudiness, even if you’re not experiencing obvious symptoms.
Can cataract surgery be performed on one eye only?
Yes, cataract surgery is commonly performed on just one eye when only one is affected. If the other eye develops a cataract later, it can be treated separately.
Can children or young adults get cataracts in one eye?
Yes, children and young adults can develop cataracts, often due to genetics, trauma, or medical conditions. These are called congenital or pediatric cataracts and may affect one or both eyes.
What happens if I delay treating a cataract in one eye?
You should consider treatment when the cataract begins to affect your vision and daily activities. Delaying treatment could lead to worsening vision in the affected eye, which may impact depth perception and daily activities. However, cataracts usually progress slowly, so your eye doctor can help you decide the right timing for treatment.
Can I drive safely if I have a cataract in one eye?
It depends on how much your vision is affected. If your vision in the healthy eye meets legal driving requirements and you feel safe, you can drive. However, always consult your eye doctor and follow local laws.
Find Out More About Your Options
Don’t let cataracts control your life. Schedule your consultation today if you’ve noticed any unusual symptoms or if it’s time for your next comprehensive eye exam. Our helpful and knowledgeable staffs at Griffey Eye Care are available to answer all your questions. And they are happy to book you in for a time that’s convenient for you.
Read About: Does Medicare Cover Cataract Surgery?
**Please note that the suggestions provided in this blog are for general informational purposes only and may not be suitable for your specific insurance plan and eyecare needs. It is important to consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment.